Some Basics about the Alternator Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR)
What is an alternator Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR)?
An automatic voltage regulator (AVR) is an electronic device that serves to regulate & maintain the output voltage of the alternator at a set value. It will try and do this as the alternator load or operating temperature changes. The AVR is part of the alternators excitation system.
AVR (Automatic Voltage Regulator) in an alternator is not only to stabilize the output voltage of an electric alternator, but also has various other functions like:
a. As a Device to adjust the output voltage (Output Voltage) of alternator.
b. As a stability and regulator of Droop Voltage for Alternators that are run in Parallel (Synchronous Alternator).
c. As a safety system over Voltage (Over Voltage) and Load or Overcurrent (Over Current) that occurs in the Alternator.
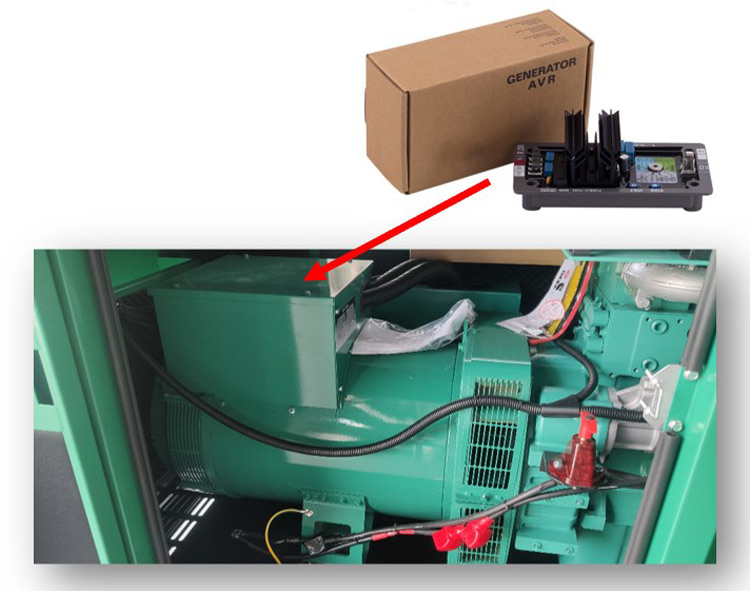
Where can you get an AVR?
Generally, the AVR will come with the AC alternator supplied by the alternator manufacturer. As we know, currently the biggest manufacturers of alternators for dg sets are Stamford AVK, Leroy Somer, Mecc Alte, WEG, ABB, etc. The model supplied will depend on the alternator and any accessories fitted to it, which may need a different AVR. An example of such accessory would be a PMG or auxiliary winding. You can also get it from dg set suppliers or spare parts suppliers.
What is the location of an AVR in an alternator?
Usually, the alternator AVR is located in one of three places.
a. In the main control box of the alternator.
b. In the alternators terminal box.
c. Could be (only on very small portable units usually) located under the alternators rear cover.
How does an AVR work?
It controls output by sensing the voltage from the alternator terminals and comparing it to a stable reference. Then, the field current is adjusted by increasing or reducing current flow rate to an exciter stator by using an error signal, which in turn causes a lower or higher voltage at the main stator terminals.
What does an AVR look like?
There are many AVR brands, but AVR's all look remarkable similar. They vary a bit in size and color, but seemingly all have similar features. Below are some AVRs of different brands:
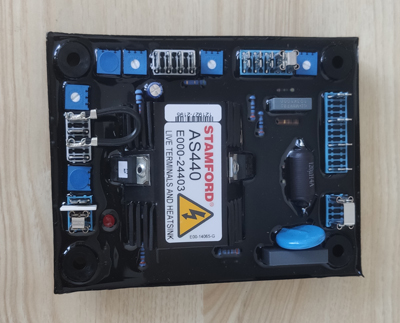
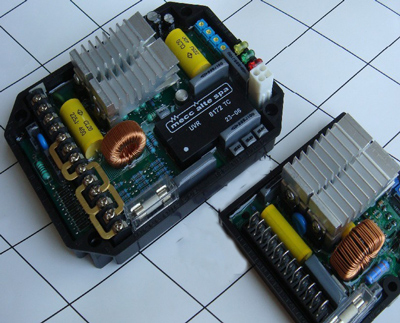


What happens if an alternator AVR fails?
If the AVR on the alternator fails, the alternator will lose excitation. This loss of excitation will cause the voltage to fall suddenly at the alternators and this loss of voltage should cause the alternator to shut down on an under-voltage fault. If the alternator does not have under-voltage protection set, then the alternator may continue to run, which might cause severe damages to the related equipment.




