The Overall Structure of Diesel Engines
The Overall Structure of Diesel Engines
Overall structure: one body, two mechanisms & five systems.
1. One body: include cylinder block, cylinder head, crankcase & oil pan.
Functions of each part:
a. Cylinder block:
a1. As diesel engine frame;
a2. For installation of important components;
a3. as main components for power generation.
b. Cylinder head:
b1. To seal the upper plane of the cylinder;
b2. To form a combustion chamber with the cylinder wall and piston top.
c. Crankcase:
c1. To install the crankshaft activity space;
c2. To bear the reciprocating movement of the connecting rod.
d. Oil pan: to store lubricant.
2. Two major mechanisms: crank connecting rod mechanism & valve timing mechanism.
1) Crank connecting rod mechanism:
Functions:
a. To turn the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotational motion of the crankshaft;
b. To turn the force of the gas acting on the piston crown into a torque to perform external work.
Composition:
a. Piston connecting rod group (including piston, piston ring, piston cutting, connecting rod, connecting rod bush, etc.);
b. Crankshaft flywheel group (including crankshaft, flywheel, torsion damper, belt pulley, timing gear, etc.).
2) Valve timing mechanism
Functions:
a. As the control component of the diesel engine ventilation;
b. To open and close the intake valve and exhaust valve regularly according to the working order to ensure sufficient intake and waste gas exhaust.
Composition:
a. Valve components (intake and exhaust valves, valve springs, spring seats, valve lock plates, valve oil seals, valve seats, etc.);
b. Rocker shaft assembly (tap rod, push rod, bolt, adjusting bolt, rocker shaft, cylinder head bolt);
c. Gear shaft assembly (gear shaft, gear shaft sleeve, timing gear).
3. Five major systems:
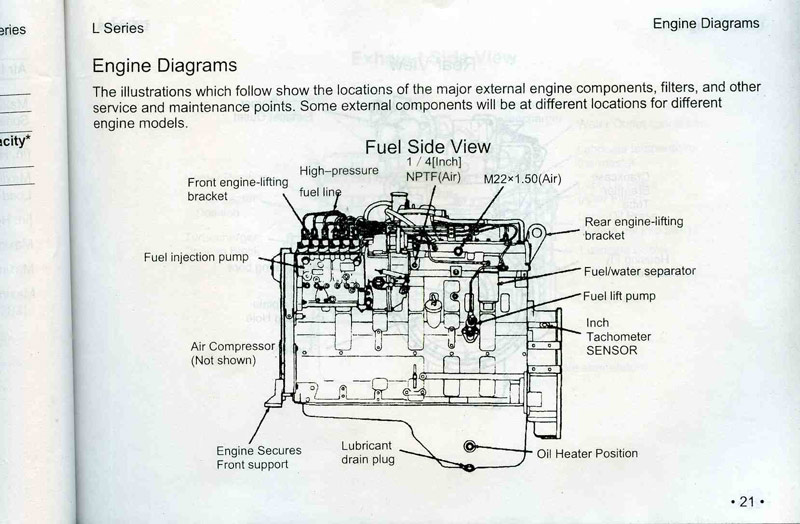
1) Fuel supply system (also known as fuel system)
Functions:
a. The volumetric air pressure is injected into the combustion chamber with a certain injection quality;
b. It mixes and burns quickly and well with air and finally discharges exhaust gas.
Composition:
a. Low-pressure part: fuel tank → oil-water separator → coarse and fine filter → fuel pump → high-pressure fuel pump → fuel injection nozzle → inlet cylinder, except for water pump. Drag by the high-pressure oil pump wheel.
b. High-pressure part: high-pressure oil pump → fuel injection nozzle → cylinder
Types of high-pressure oil pumps:
a. Plug type (Bosch type) oil pump;
b. Distributed oil pump.
Types of fuel injectors:
a. Hole injector;
b. Axle needle injector (all are closed injectors).
2) Lubrication system:
Functions:
a. to reduce friction; b. to transfer heat and cool; c. to seal; d. to clean.
Methods:
a. Pressure lubrication; b. Splash lubrication; c. Gravity lubrication; d. Calcium-based lubrication.
Composition: oil pump (gear type & rotor type) → oil fine filter → enter the body oil passage, pressure limiting valve, oil radiator, oil, oil pressure gauge, oil cooler. The oil pressure is 0.4rpa~0.6rpa.
3) Cooling system:
Function: to ensure that the temperature of the unit is controlled between 80°C and 90°C (normal temperature: 85°C).
Methods: a. air-cooled; b. water-cooled (water-cooled implements forced circulation:
b1. Large circulation: passing through the water tank radiator;
b2. Small circulation: not passing through the water tank radiator.
Control of large and small cycles: controlled by the thermostat, and the opening temperature of the thermostat: 26℃.
Composition: water pump, radiator, fan, water tank, thermostat, coolant (soft water is required, so add glycol).
4) Starting system:
Functions: to start the engine quickly, stabilize idle speed, transmit torque and start the host.
composition:
a. Starter (also called motor), DC motor plus starting mechanism;
Voltage: 12V~24V; power: varies with different models.
b. Battery voltage: 12V~24V.
5) Intake and exhaust system:
Functions:
a. To supply clean, dust-free, high-density and high-definition air to the diesel engine;
b. To remove exhaust gas from the cylinder.
Composition: Air intake: air filter ~ intake pipe ~ exhaust gas turbocharger ~ elbow ~ intake cylinder
Exhaust: Exhaust~Exhaust pipe~Muffler




